A corrupt banker, Sir Henry Furnese, was the first documented person described as using business intelligence. In 1865, Richard Millar used the phrase “Business Intelligence” to describe how Sir Henry used fresh information about the political market to win a bet against his competitors.
Since then, BI has slowly been adopted in various other industries for honest causes, with a boom in the 1990s. Although BI is still in its early stages, several industries use it to improve their business outcomes. In this article, I'm going to walk you through how 12 major industries are taking advantage of BI.
What is Business Intelligence (BI)?
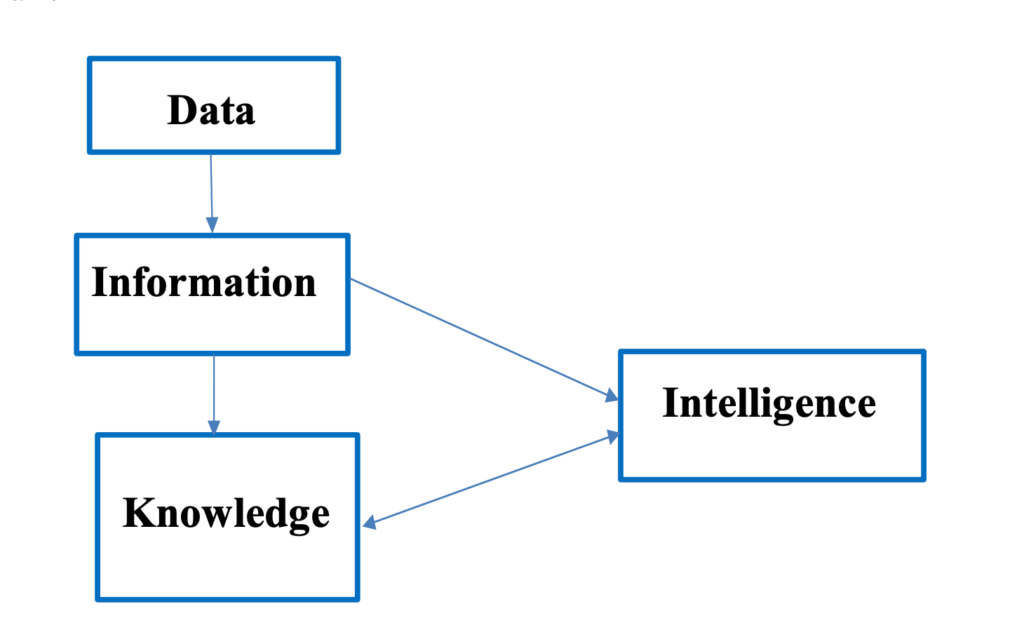
Business Intelligence is the process of collecting and using accurate data and empirical evidence to make informed decisions. It involves ingesting data from different sources, transforming and processing it, and visualizing it for analysis.
BI also includes performing experiments to test hypotheses and segmenting users for tailored analysis.
How Can BI Help Businesses Make Decisions?
It’s important to know BI is used interchangeably as a system and a process. Ideally, BI is the process of using data to make business decisions. However, people refer to BI tools as BI alone. So, every time I use BI, I refer to both the process and systems used.
BI speeds up the process of decision-making in five steps:
- Data integration and collection: Business intelligence software automatically ingests millions of data (big data) from numerous sources, making the relevant data available for faster decisions. Some tools also ingest real-time data and automatically effect changes.
- Data storage: Some BI Platforms have in-built data warehouses for data storage.
- Data preparation and transformation: BI systems have scripting and coding environments to prepare and transform data. You can also use no/low code features like a drag-and-drop tool to transform data without BI specialists and devs.
- Data visualization: Using charts, graphs, and interactive dashboards, you can use BI tools to visualize your transformed data. This makes it easier to perform analysis and understand your data.
- Data experimentation: Some BI tools like Amplitude have in-built experimentation platforms where you segment data and perform tests on hypotheses.
On top of that, businesses use BI principles and procedures to make better data-driven decisions.
Which Industries Use Business Intelligence?
BI has many benefits so it's used in many industries, but in this section I’m going to cover the 12 most prominent ones.
Most of these industries use BI for the same primary reason. To collect data from different sources relevant to their industries, analyze this data, make better data-driven business decisions, and improve business processes.
The difference is in the data sources and kind of business decisions.

1. Financial Services
The finance industry includes banks, credit unions, stock brokerages, accountancy companies, insurance companies, and others. Finance professionals use BI for the following purposes:
- Financial Management and Analysis: BI ingests and consolidates raw data needed to create, plan, and manage financial assets in an organization. Experts collect this data from sources like Excel, CRMs, financial management systems, payroll software, invoicing systems, etc.
Post-collection, professionals use BI to analyze customer behavior, forecasting, past performances, risk profiles, revenue analysis, etc.
For example, it’s instrumental in lending sectors for assessing credit risks. With loan defaults witnessing an alarming spike, it’s not surprising that creditors want to protect themselves. How it works is simple.
Banks or peer-to-peer lenders integrate BI software with their proprietary platform. Then, the tool receives information about applicants, such as credit scores, income, employment, and lending history. This data tells them whether applicants are high-risk defaulters or not.
The software segments applicants compares their data, and helps banks decide whether applicants are eligible.
- Accurate forecasting and reporting: BI automatically generates reports based on certain parameters after analysis. For instance, you can automatically generate monthly or quarterly statements for customers. This way, you save time and cut out manual work.
It took a day or less for Tandia to create financial reports with BankBI, which usually took days. They could consolidate data from several sources and analyze them easily instead of using Excel sheets.
Another notable use case is real-time updates. The finance industry leaves no room for inaccuracies, which is something BI systems make sure of. Most of them can plug into cloud services, databases, Application Programming Interface (API), web apps, and numerous channels to fetch data seamlessly.
Let's say you want to track stock prices and trade volumes. Your BI solution can instantly connect with stock market APIs, like Yahoo Finance, and retrieve the needed data.
Glide Invest faced an issue with such heavy data importation. They brought customer information from the Zoho CRM, Zoho Desk, and even Facebook. But they couldn’t blend it together in a simple and fast way.
The solution was Zoho Analytics, a software that automated data collection from multiple channels and displayed it on a central dashboard in minutes.
- Data compliance: The financial industry is heavily regulated because of how sensitive currency matters are. BI tools ensure that institutions adhere to laws that govern them. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) states that consumer data must be "processed lawfully, fairly, and in a transparent manner in relation to individuals."
A bank configures BI systems to log activity to comply with this regulation. Systems create a timestamp and record the dates when staff access customer information.
The bank also segments customers, encrypts their data and restricts access to authorized personnel. Should an unauthorized person try to reach it, they trigger an alert.
2. E-commerce
Online store owners use BI in several ways to improve business efforts. Some of them include the following:
- Data consolidation: Businesses use BI to collect customer and sales data, such as names, addresses, purchase histories, supply chain data, bounce and click-through rates, etc. The system retrieves them from mobile apps, point-of-sale (POS) systems in physical stores, social media, and other channels. Then, it displays them in one place. Tools like ScienceSoft even have features that pull comments, reviews, and other soft data from the web.
- Data analysis: BI provides the tools needed to analyze data, like visualization tools and artificial intelligence. Allowing e-commerce owners to understand customer and competitor behavior and make better decisions. BI is used for data mining, where you sort through large datasets to identify patterns in the data.
- Sales forecasting: BI can be a crystal ball for forecasting sales and making projections. Collecting past and current customer data helps you understand their buying pattern and predict what they’re most likely to purchase in the future. If your software tells you they’re spending on Winter coats, you stock the most and focus advertisements on that. Tools like Powerbi allow you you to develop and train your machine-learning models to make sales predictions.
- Personalization: it benefits both ecommerce owners and customers. On the business owners' part, inventory management becomes seamless. You can track which products have high demand and restock them accordingly. For customers, you can offer better recommendations based on their demographics and other metrics.
- Reporting and collaboration: E-commerce teams use BI systems' reporting and dashboard features to share insights with colleagues and stakeholders. Internal teams collaborate better because they can view data simultaneously, ensuring they align on the same overarching goals. You can also track relevant KPIs on your dashboard automatically.
3. Education
Schools improve student support, curriculums, and resource allocation with BI. It's beneficial in the registration process, especially for higher institutions that deal with an influx of applications per semester. Administrators will know which courses to prioritize and design a schedule for popular choices.
St James’ Independent Schools once struggled to sort student data and share it with stakeholders. With SchoolsBi, they segregated the data into parameters clearly pointing out student attendance, behaviors, and sanctions. The South East London Academy Trust (SELCAT) also found it easier to answer pressing questions they had concerning resources and planning.
That said, BI aligns expectancies with the available resources and ensures you don’t waste resources. You’ll know the right questions to ask and make decisions that affect everyone positively. For instance:
- How many classes are students taking?
- How many teachers are available?
- When are the teachers due for a leave?
- Do they have the capacity to take on more workload?
- What are the rehiring costs if they quit or get fired?
- When would we need a substitute?
Even online learning platforms use business intelligence platforms to track how learners engage with their platforms. How many students use in-software notes? Does video length affect engagement? What factors affect engagement? All these help with predictive analytics, where online learning platforms forecast how to improve their software for better learning outcomes.
In-built visualization tools are also used to explain findings to decision-makers.
4. Government and NGOs
Concrete data is necessary for making city or nationwide changes. It also helps to tackle unforeseen circumstances. When faced with a crisis, governments are better equipped to quickly counter-responses.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Taiwan used data sciences, advanced analytics, and database linkages across governments to get deep insights into cases and develop safety policies. Because of their early response, they slowed down the first virus wave and prevented a catastrophic local outbreak.
But the government is broader than it appears. It mixes military, law, public health, transit, public education, and more sectors. So there’s an overlap with how BI is used in government and other industries.
Governments and NGOs often use it to gauge their decision-making process, performance gaps, successes, and failures. They establish KPIs aligning with their objectives and track progress towards accomplishing them.
To reduce crime rates, governments first need to look at total reported cases, types, assaults per number of residents, and the average response time from law enforcement, among other factors. Afterward, policymaking can commence.
Regular analysis tells them if they're making progress or not. Higher numbers mean they need to reiterate and make better policies. Lower rates mean that their current strategy works.
For Non-government organizations (NGOs), fundraising for initiatives is the goal. But not everyone is a donor. BI data helps them analyze individuals with more potential and tailor a campaign that appeals to the target.
In the aftermath, they can provide transparent data to the donors, beneficiaries, and the public on spending compared to the initial budget. Using such data-centric solutions is what helped the UN World Food Programme streamline its processes and save over $130M.
5. Hospitality
Peak and off-peak periods can make or break business for hotels, recreation, tourism, and entertainment services. Navigating them is tricky, considering the demand fluctuations.
While the temptation to leap into excessive advertising and overstaffing is strong, it consumes the budget and may even lead to marketing fatigue. However, BI ensures that there's a balance between competitive pricing and customer experience.
Business owners can set a dynamic pricing range within their system, and the software knows how to adjust rates based on the demand. These changes occur in real-time and synchronously so that every booking platform reflects the same thing and you don't confuse customers.
1834 hotels used Qlik to solve their biggest challenge: gathering real-time room supply and demand data. In doing so, they also saved two days they would've spent on data compilation.
6. Fashion and Retail
Trends, competition, and rapid changes characterize the fashion industry. Designers constantly face pressure to create the season's next "it" look. BI helps them stay up-to-date via tracking sales records, ERP, social media, and fashion publications for current market trends.
If the color black is a popular topic across all channels, designers receive a ping on the software. Eventually, their creative process surrounds making fashion pieces that feature the trending color.
Overstocking is another huge problem BI solves. Brands use artificial intelligence, the software's demand forecasts, and omnichannel synchronization to streamline business operations, prevent excess leftover pieces, and incurring costs. Lead intelligence, customer loyalty
7. Human Resources
Human resources professionals use BI in talent acquisition to review and compare resumes and for recruitment automation. Then pick the top job applicants based on predefined criteria. They also monitor turnover trends and employee feedback to create an internal culture that boosts retention. Other uses for BI in HR include
- Training and development: HR managers design training programs and measure effectiveness with BI software.
- Appraisals and rewards: Managers monitor the progress of employees and reward them.
- Mergers & Acquisition (M&A): merging companies can fuse existing data, such as employee demographics, compensations, roles, and performance history, into a unified system.
8. Manufacturing
Manufacturers use BI to make cost-efficient decisions. The software compiles data from multiple warehouses, suppliers, and partners and silos it into one accessible source.
Departments can reach it at any time and reduce bottleneck effects. They’ll know when there’s equipment or employee downtime and react immediately so that production continues.
Externally, manufacturers monitor partners or supplier metrics to determine relationships. E.g., delivery timeliness, product quality, and costs. Regarding risk management, BI checks weather forecasts, inventory levels, and customer trends for potential bottlenecks.
Having this foresight helps manufacturers create backup plans and avoid disruptions. In a similar fashion, Capital CS used Phocas to make speedy predictions of dramatic changes in the steel market.
BI also helps manufacturers remain compliant with the law. You configure what the software should watch out for, such as waste disposal, energy consumption, workplace accidents, and tax irregularities.
When you cross a limit or come close to breaching regulations, the software sends you warning alerts. This way, you catch issues before they escalate rather than after.
9. Media and Entertainment
One of the biggest challenges in the entertainment industry is data variety and data management, a problem Multimedio solved with a BI solution. Media is expressed as music, podcasts, movies, or long-running TV shows and in vast volumes. Sorting through this data is tasking and takes time.
BI tools are capable of unifying and properly arranging them. Streaming services also use it to make movie recommendations for users. They collect data on what shows you watch, for how long, and the categories. So when you view Adventure movies, you’ll receive notifications to watch new adventure releases.
With cinemas and live theater performances, it helps with pricing optimization and ticket sales. They'd know which genres perform better and what people prefer to watch in varying seasons.
10. Healthcare and Medical
BI uses in healthcare spread across pharmaceutical services, medical research, telemedicine, patient care, and staff training. Integrating healthcare and business intelligence is often tricky because of how sensitive medical records are.
As patient-doctor confidentiality clauses exist, many organizations may have concerns about data breaches and privacy violations. Luckily, they can fine-tune their software to comply with governmental acts like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
BI promotes personalized treatments. First, providers unify scattered data from electronic health records, lab results, and patient histories. Then they gain actionable insights like illness patterns, risks, and the best treatment plan forward. ThoughtSpot enabled Accelerated Pharma Leader’s access to data, making it easier for them to decide on drug trials.
Studying these patterns also allows them to watch for irregularities or false symptoms. Thereby measuring real versus false cases and saving time with resources.
More Articles
- The 17 Best Account Management Books to Master Client Journeys
- What is Sales Forecasting? Your Key to Informed Decisions
- What is CPQ: A Guide to ‘Configure, Price, Quote’ for RevOps Teams
- 4 Benefits of Conversation Intelligence Software: How Can It Enhance Your Operations?
- 18 Business Intelligence Books You Can’t Miss
11. Telecommunications
Business intelligence solutions solve numerous problems for telecom providers. They look out for network congestion, connectivity, and call drop rates that interrupt customer conversations and lead to churn.
Verizon saw it as a way to segment customers, understand them, and reroute their calls to the appropriate specialist. Tableau helped them reduce support queues and unnecessary repeat calls.
BI also studies user call patterns and contributes to fraud detection systems. Providers are able to fish out SIM card cloning cases and other anomalies.
They monitor unusual user patterns, such as excessive international calls, dialing different numbers simultaneously, multiple SIM cards using the same identity, etc.
12. Transportation
BI assists airlines in increasing their revenue streams. A good case study is how Dubai Airports used Tableau to attract more airlines, expand their routes, and satisfy customer needs.
Identifying those needs required intense data crunching, which was manual and took days to parse the data. The risks of overlooking potential opportunities were also high.
With BI software backing them up, they streamlined data analytics and met customer needs quickly.
Other transportation sectors use BI for route optimization and fleet management. Delivery services often use BI to gauge weather conditions and GPS in recommending the best routes for drivers.
In fleet management, the software gathers sensor and GPS data to evaluate driver performances. Business owners use the information on speed, braking, and fuel consumption to make maintenance cost-reduction decisions.
Adding BI To Your Business
After reading about how these 12 industries use BI, you may want to join the BI Bandwagon. However, don’t hop on the trend without clearly defining your BI strategy.
To start, identify your BI maturity level, understand why you need a BI solution, set SMART goals, set your budget, select a BI tool based on your need (preferably self-service BI tools), and then measure your progress and iterate.
While you’re here be sure to check out our article on sales intelligence, and subscribe to our newsletter to keep up with important information about BI and other ways to improve revenue strategy. Join our community of intelligent business leaders like yourself who are passionate about RevOps, and get all the latest straight to your inbox.